Inhaltsverzeichnis
In our today’s increasingly digitized world, in which new technologies are constantly being developed further, we are increasingly confronted with concepts such as virtual reality and augmented reality. But what do these two terms indicate? And what exactly is the difference?
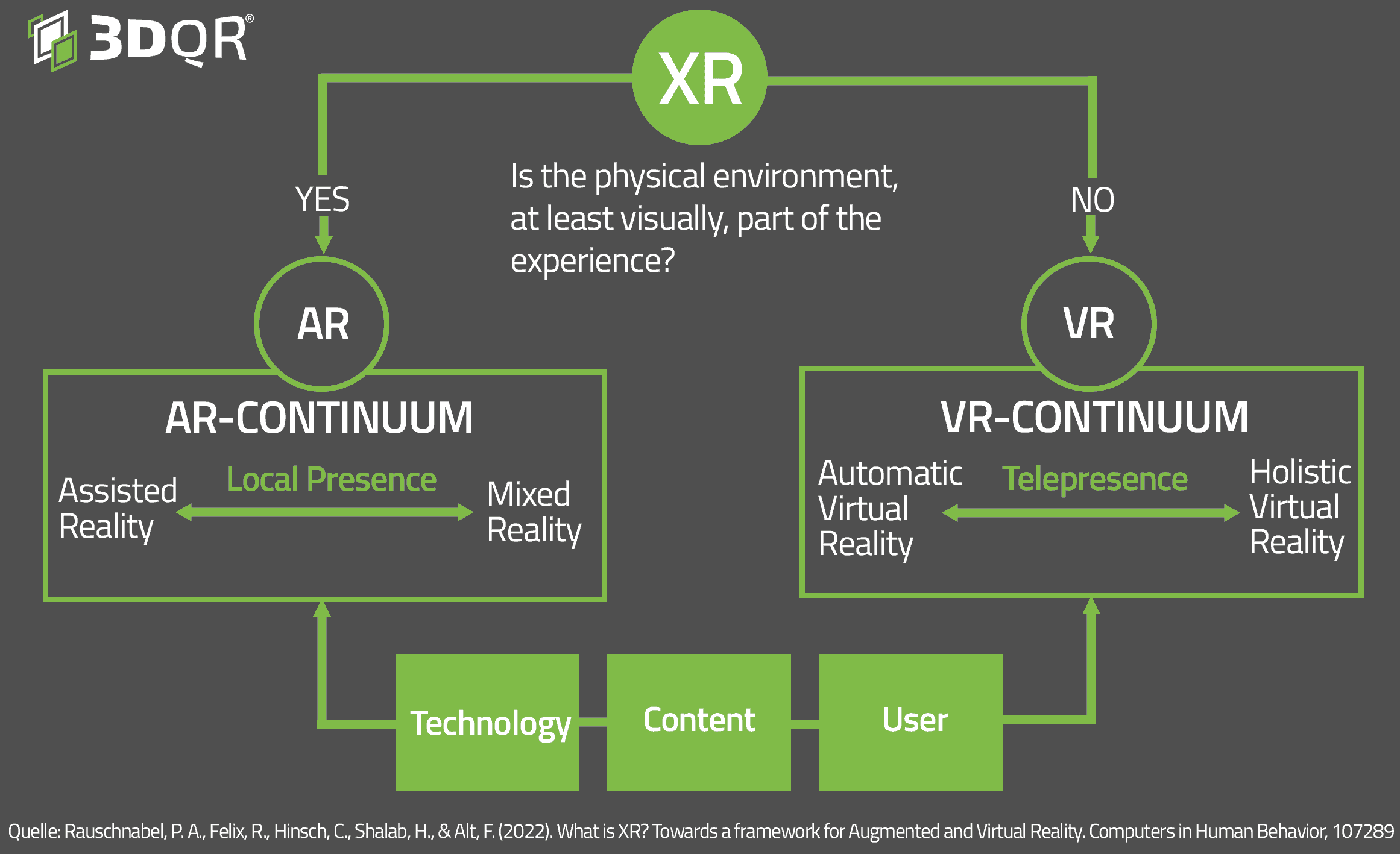
Basically, we can say that both technologies have a direct effect on our personal perception. Both, VR and AR, represent increasingly important instruments in our economic world, whereby Virtual Reality is understood as a more extreme version of reality simulation. Thereby, our entire environment is simulated virtually by means of computer technology.
The second and less extreme kind of perception extension is Augmented Reality. AR is a form of Mixed Reality, but differs minimally from it. As the name “augment” suggests, AR technology, unlike Virtual Reality, does not transport individuals into an entirely new world, but merely projects individual artificially created objects into our real world. With Mixed Reality, there is also the added possibility that the contents in the real and in the virtual world can interact with each other. This is not the case with Augmented Reality.
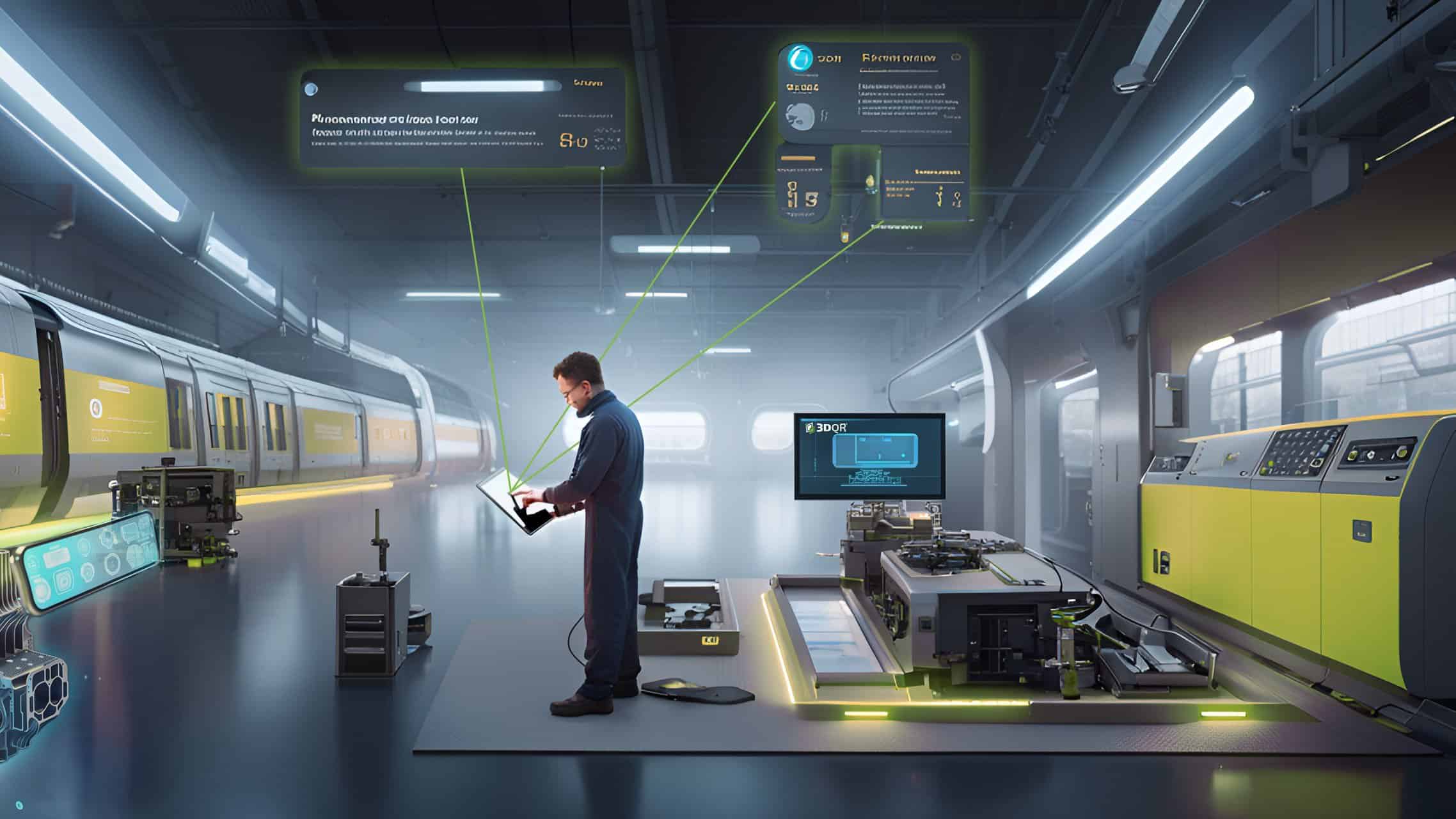
An increasing number of companies are currently dealing with all these emerging markets of reality simulation. The company 3DQR, for example, has set itself the goal of significantly facilitating everyday work in various industries by means of 3D models. 3DQR has put a special focus on Augmented Reality.
As a prominent application example for Augmented Reality, the well-known mobile game Pokemon GO can be named, in which fantastic creatures from all over the world can be developed, tracked and made to fight against each other. This ability to implement virtual objects into reality is probably the biggest advantage 3DQR customers can derive from the 3D models.
But also in many other industries like health care, engineering or other manufacturing sectors like automotive or architecture AR can potentially create great added value. The beginnings of Augmented Reality lies at the end of the 20th century. However, the technology failed at the first attempt due to the insufficient progress of the technology. Nevertheless, in the meantime, Augmented Reality has developed into a 27.2 billion US dollar market which promises an enormous success for the future.1
Another emerging sector of this industry is the already mentioned market for Virtual Reality which comprises a size of 13.1 billion US dollars.1 One of the most popular examples of this technology are the VR glasses through which one can immerse oneself in a whole new world. Thus one can be mentally teleported into any imaginable scenario.
The origins of VR can be traced back to Morton Heilig, who developed the so-called Sensorama in 1962. With this revolutionary invention all senses were artificially manipulated simultaneously for the first time. For example, the ride on a motorcycle could be imitated by creating a 3D view of the roads, making seats vibrate and even imitating scents and noise.
However, as the true founder of the VR system as we know it today can be seen Ivan Sutherland. He developed the first VR headset in 1968. However, with regard to the history of VR, it was not until 1987 that the term Virtual Reality was first used in today’s sense.
In research and science departments at the university, however, this new progress was initially not used as a product for everyday use, but only to explore the limits of our human perception. Still, in the following years global players such as Nintendo and NEC tried for the first time to establish this application in the consumer market. Nevertheless, due to inadequate technological development, these attempts failed at that time and came to a temporary standstill again.
In the meantime VR has developed into an extremely promising and valuable tool for gaming, industry, architecture, real estate, medicine, sales, education and many other areas. The company 3DQR in cooperation with the Fraunhofer Institute IFF and a metal foundry has also carried out a progressive project which had the aim to use a new, innovative testing tool to replace a current, demanding production process. In order to better identify the existing problem and the potential for improvement, the company developed VR scenes that visually depicted the current situation as well as the planned situation. For this VR scenes developed and presented by the Fraunhofer IFF at the Hannover Messe 2019, the institute even received a prize for the best exhibition stand.
All these are indications that both VR and AR today seem to be much more efficient and feasible. This is why they are considered to have a high potential for daily use in the future. One high aiming exemplary high AR goal is to provide a lot of additional information about the environment. Only by looking at the smartphone or with the help of a computer chip implanted in the brain it should be possible in the future to communicate opening hours, offers or customer evaluations of shops to consumers.
And although the use of such chips as a matter of course still seem like a Blade Runner script today, an exponential growth in new technologies such as the iPhone has been observed in the past. Therefore, experts see enormous potential in both the AR and VR sectors. If used correctly they hope for a breakthrough by the year 2025.
One of the biggest advantages AR has over VR is the possibility that individuals can decide for themselves whether and to what extent they want to network with their physical environment. In contrast, VR has the effect of isolating oneself from the real world and acting exclusively in an artificially created reality.
To sum it up, for these technologies it can be said that AR glasses represent a particularly powerful alternative to VR headsets and conventional working tools. They provide the employee with the right information at the right time in the ideal format. At the same time, AR is leaving workers’ hands free so they can work without interruption. This feature makes augmented reality such a promising instrument for the industrial future.
1 Deloitte Insights: Technavio, “Global augmented reality market – 2017-2021,” 2016, p.33; Technavio, “Global virtual reality market – 2015-2019,” 2015, p.19; Technavio, “Global mixed reality market – 2017-2021,” 2016, p.27.