Close
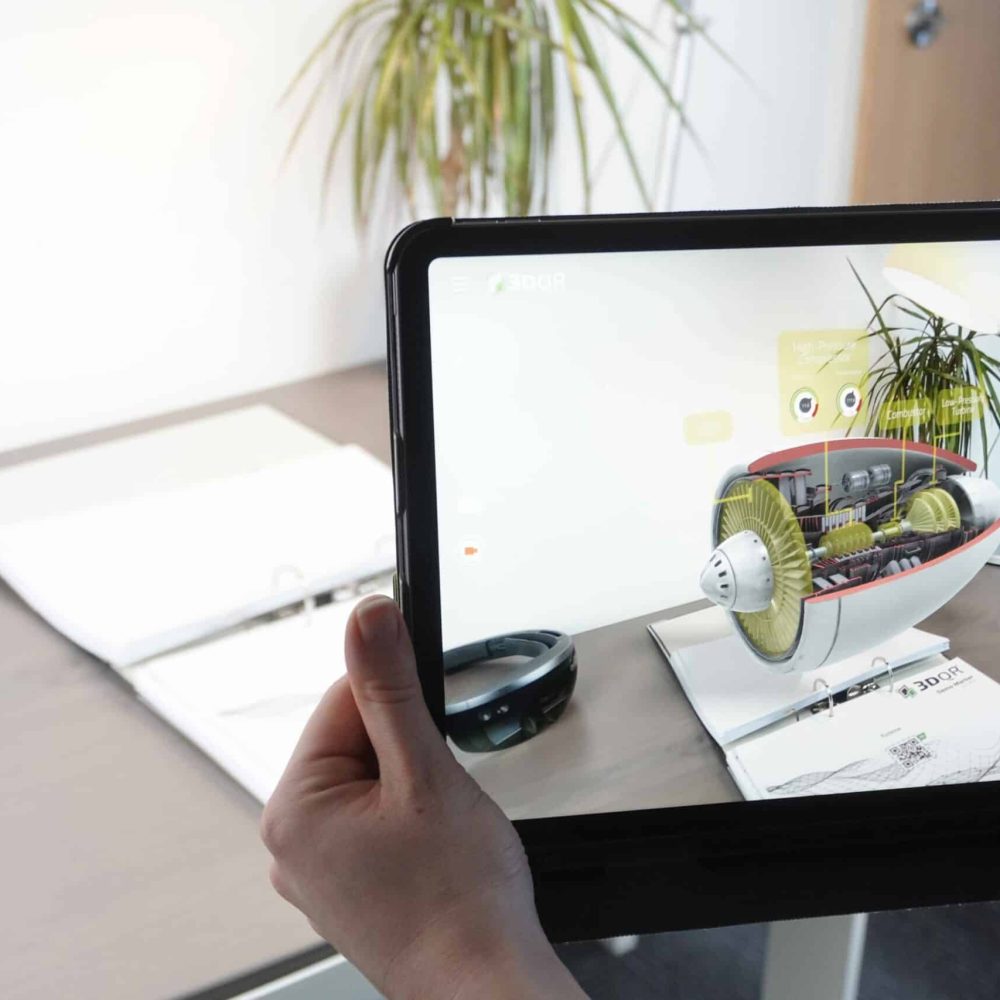

Augmented reality refers to a computer-based extension of our perceptible reality. Generally, all human senses are addressed, but often it is only about the visual or auditory depiction of information, i.e. in the form of an overlay. A commonly known example is the arrows and rings used in the analysis of soccer matches.
Augmented reality is a valuable tool for displaying digital information, objects or data without requiring users to look at a computer. The main advantage over virtual reality is that with AR, reality is still perceptible. The user still has the familiar capability to react to outside stimuli. AR visualizations immerse you in a hybrid world of completely virtual content and the real environment, where you experience events from reality, enriched with digital elements.
Scenarios in which augmented reality is used are versatile and have different added value. Three areas where AR has many applications are marketing, education, and industry/trade. As technology advances, the possibilities AR offers will only become more numerous and impressive thanks to hardware like AR glasses. But what is already feasible with good tracking software and smartphones, we showcase in the upcoming segment.
In industry, augmented reality offers many capabilities, opportunities, but also challenges. However, AR has one important goal above all in this area, namely to increase the efficiency of operational work in plants. Maintenance and servicing are just one example where the documentation of necessary work steps in the form of step-by-step instructions in AR directly mounted onto the machine, let the error rate drop by up to 80%.
Exploring and trying out AR scenes is also central to education and offers many advantages over non-fiction books and educational films. Education here means school-based, but also adult education. Augmented reality appeals to all senses, apart from touch, and creates a visual and auditory experience that can be discovered in three-dimensional space. The fact that addressing multiple senses has been proven to guarantee a high level of learning success is something that everyone has already experienced for themselves.
In advertising and marketing, AR as an interactive medium offers a great advantage that video and audio do not have. As we can see from the huge success of Instagram and TikTok, Interactivity is a unique selling point that is not to be underestimated. Both social media apps are used worldwide thanks to fun interactive effects which make the generated content more share- and likeable.
Augmented reality (AR for short) comes in two different types. One is Web AR, which does not require an extra application on the hardware and has all the data computed in the cloud. The other type is app-based augmented reality. But what exactly does this mean for the user of augmented reality content?
If one wants to make an AR application accessible to as many as possible, web AR seems to be the obvious solution, since the only prerequisite is that the end device supports a browser. An app, on the other hand, must be supported by Apple’s App Store or Google’s Playstore. But what are the disadvantages?
The first noticeable disadvantage is the level of detail of the graphical display. An app installed on the smartphone or tablet can take full advantage of its performance and runs more smoothly due to local calculation. The same applies to the tracking software, which makes it possible to move more smoothly through an AR scene. Above all, however, offline functionality is of utmost importance, since not everywhere AR is used internet is also available. So if you want to display a stable and interactive AR scene, you are much better off with an app.
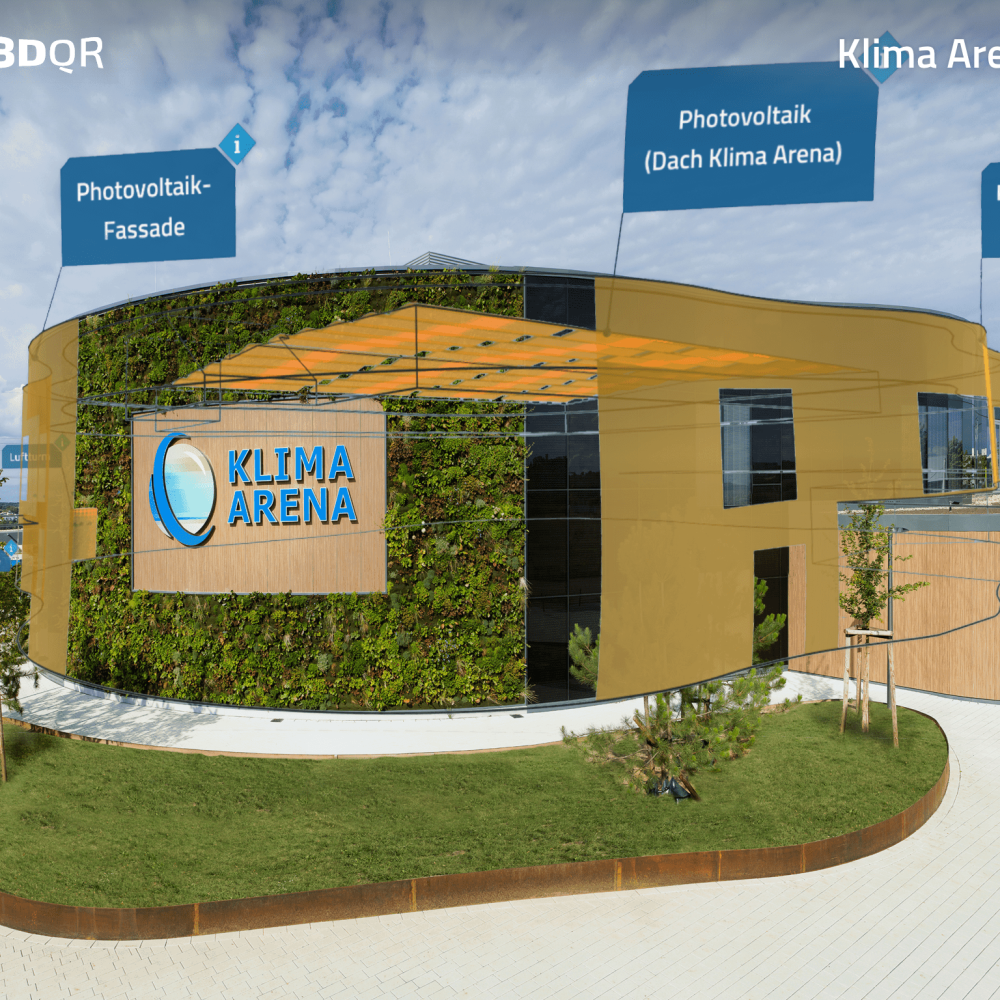

ARKit and ARCore are among the most popular tools that facilitate the development of an augmented reality app. Thanks to these SDKs (software development kits), programmers can start developing their ideas right away and don’t have to dwell on the basic building blocks. While all of these tools have good capabilities to offer, there are small differences that developers need to know and consider when choosing the right tools, frameworks, and SDKs for AR app development!
The main advantage of ARKit for developers over other popular AR development tools is the Apple ecosystem, which makes development easier. It also offers frequent updates and new features for more exciting app development possibilities. But as mentioned earlier, a major limitation of the ARKit for app development is the fact that its use is limited to the iOS platform, i.e. iPhone 6s+ and iPad Pro+ only. Also, it cannot perform motion capture for very fast movements.
ARCore is Google’s toolkit (framework and SDK) for building augmented reality apps. The best thing about ARCore is that it supports development for Android as well as iOS platforms. Moreover, this AR development toolkit is available for free! ARCore offers points, layer detection, pose, light estimation, anchors, image tracking, face tracking, object occlusion, and cloud anchors. These capabilities and results are similar to ARKit.
In principle, AR can be used to represent anything that can be visualized in any other way. Product showcases realized through augmented reality brings products directly into people’s own four walls and, unlike looking at a catalog, the objects can be viewed in 3D, so lifelike you can almost touch them.
Machine parameters are visualized through an AR device and settings changed through it are transferred back from augmented reality directly to the machine, so that workers no longer have to switch between different display media.
Other use cases can be found in education. Here, animations and interactive scenes can be accessed directly in the textbook. Step-by-step instructions can also be displayed and used where they are needed.

Together with Novoferm, we have developed an AR product configurator that lets customers make changes to the product in real time and in AR. All the customer needs is the QR code and the 3DQR Plus app. The garage door can be viewed and configured in its original size, but also in miniature.
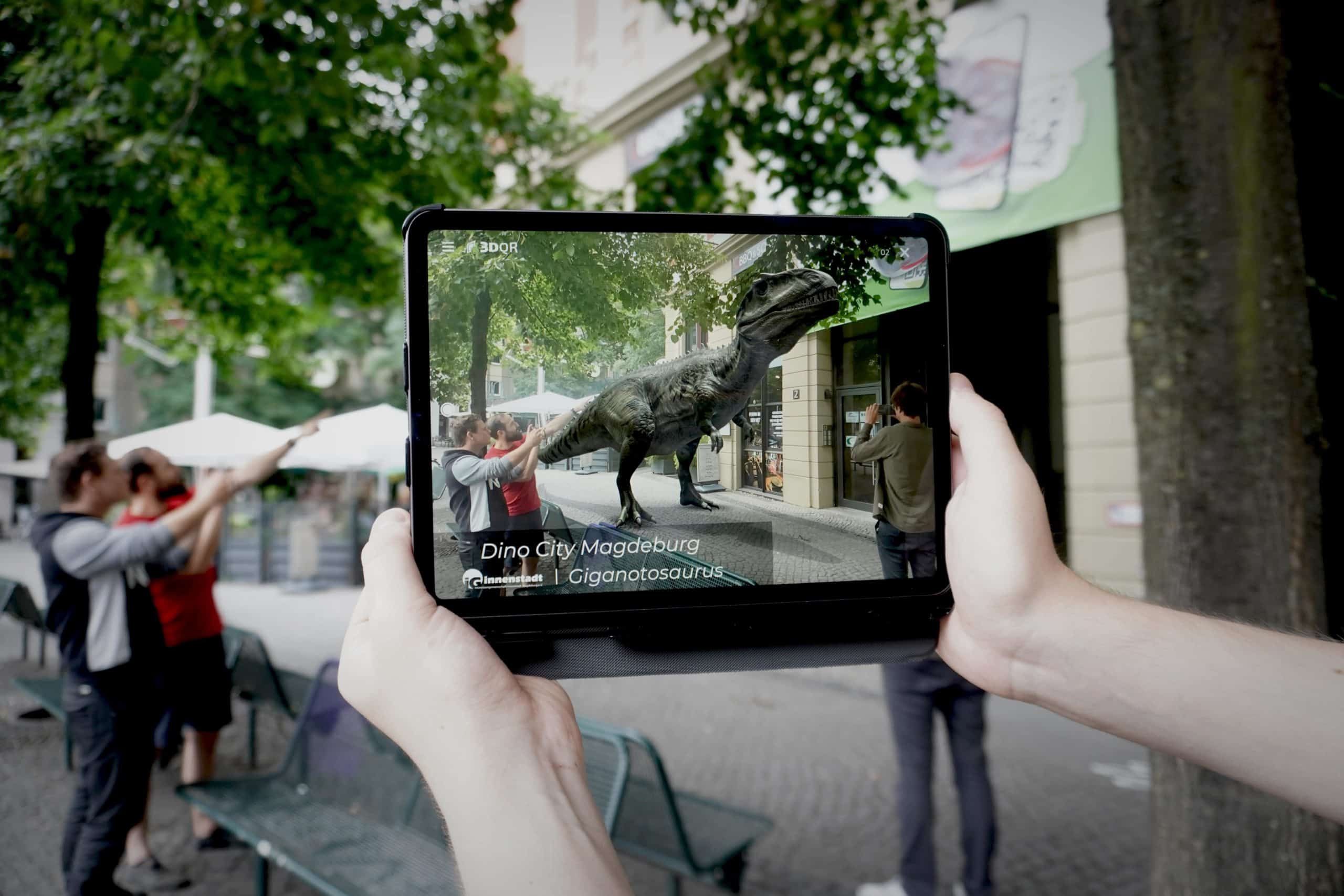

Anyone booking a vacation may be disappointed by reality, because catalogs rarely manage to depict reality truthfully. With the help of AR and 3DQR codes, three-dimensional plans of hotel facilities or entire landscapes can be recreated. Another area of application is historical sites or national parks, where augmented reality can be used to convey additional information to visitors without having to erect new information boards.
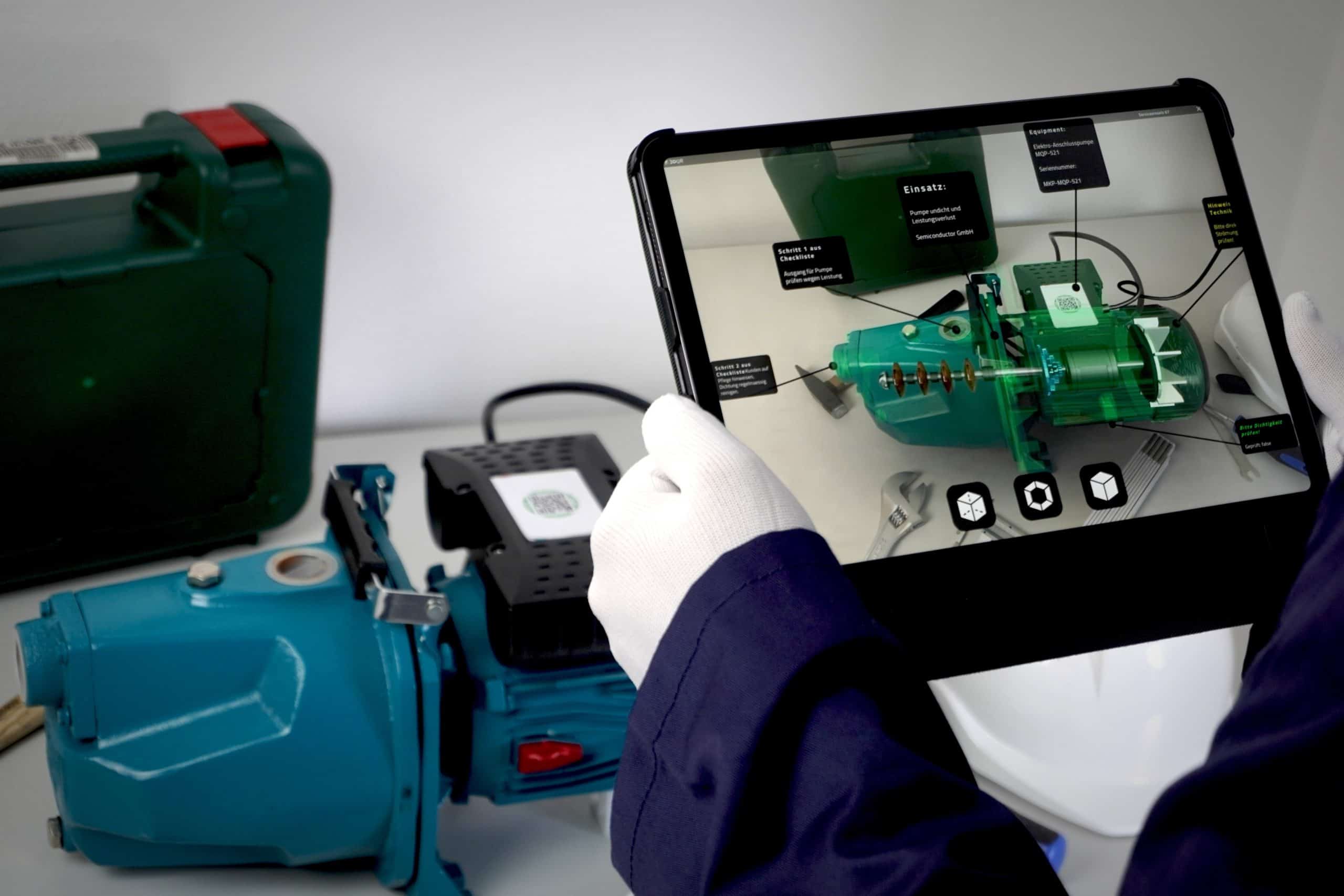

Many devices must constantly and reliably fulfill their purpose. This can only be achieved with fast and effective customer service. Augmented reality offers the perfect solution for a seamless human-to-machine interface. Together with our partner valantic, we would like to take a closer look at how 3DQR brings augmented reality to SAP Field Service Manager in this webinar.
Augmented Reality can be experienced with different end user devices. AR hardware ranges from smartphones and tablets to AR glasses and the first prototypes of AR contact lenses. The advantages of mobile devices for rendering AR lie in the wide-spread usage of them, since almost every potential user already has a cell phone or tablet, both in private and corporate environments. This means smartphone AR is much more accessible than AR solutions designed for glasses. One big advantage in using AR glasses, on the other hand, is the hands-free usability since the hardware does not need to be held. This makes them very interesting for industrial applications. All in all, AR does not have a particularly high technical requirement.
AR for cell phones and tablets is simple to explain. The camera of the smart device shows the recorded physical world on the display, enriched with digital objects placed with the help of tracking software. Everyone knows the example of Pokemon Go, where the player's surroundings are overlaid with a wide variety of monsters. However, the technology used definitely has its place in an industry 4.0 environment. Instead of in a park, AR can also be used to augment a machine on a factory floor with relevant information. The operator then only needs his cell phone to call up relevant information right on the spot without having to carry stacks of paper with him.
Apple currently offers the best solution here with the iPhone 12 and the iPad Pro variants, because these have LiDAR sensors which enable the tracking software to create an accurate image of the surroundings.
Augmented reality can also be viewed through specially developed glasses, but at the moment these are still significantly more expensive than cell phones or tablets. The development of dedicated software is also much more costly. Nevertheless, we would like to list the most popular solutions here, since they also offer a great advantage thanks to the head-mounted display.
Microsoft's AR glasses visualize a wide variety of 2D and 3D multimedia content or holograms. In 2016, the first HoloLens was sold for developers and businesses. Since 2019, however, there is also the HoloLens 2. The wearing comfort is very good due to the headband, but the price of over 3000 € is a big investment for many.
The Apple Vision Pro is a revolutionary spatial computer that seamlessly connects digital content with the physical world, allowing users to stay present and connected. It offers an infinite workspace for apps, a fully three-dimensional user interface, and is controlled by the users' eyes, hands, and voice.
The benefit of the Apple Vision Pro lies in creating a new dimension of personal computing. It enables unique experiences for users, whether in productivity, entertainment, memory management, or social interaction. With the spatial operating system visionOS and its innovative features, it opens up exciting new possibilities for developers and users alike.
The price of the Apple Vision Pro will be $3,499, and it will be available on apple.com and in Apple Stores in the USA next spring. Availability will expand to other countries later next year.
The introduction of the Apple Vision Pro signifies a groundbreaking development in the field of spatial computing. It is a milestone for Apple, setting new standards for personal electronic devices. With its innovative design, spatial operating system, and powerful features, the Vision Pro will significantly impact the computer and technology market, paving the way for creative applications and interactions.
Google's AR glasses were released for developers in 2013. Weighing only 42 grams and with a simple design, they are hardly more noticeable than normal glasses. A small projector on the frame projected an image into the wearer's field of vision. However, due to a lack of applications and privacy concerns, the project was discontinued by Google.
Magic Leap wants to combine the image quality of the HoloLens with a smaller form factor with its AR glasses. Here, a digital light field is projected into the eye to display virtual objects in the real world. Besides the glasses, a processor unit is also included that can be carried in the pocket.
This head-mounted display is aimed only at professional users in industry and research. Popular application areas here are production tasks or logistics.
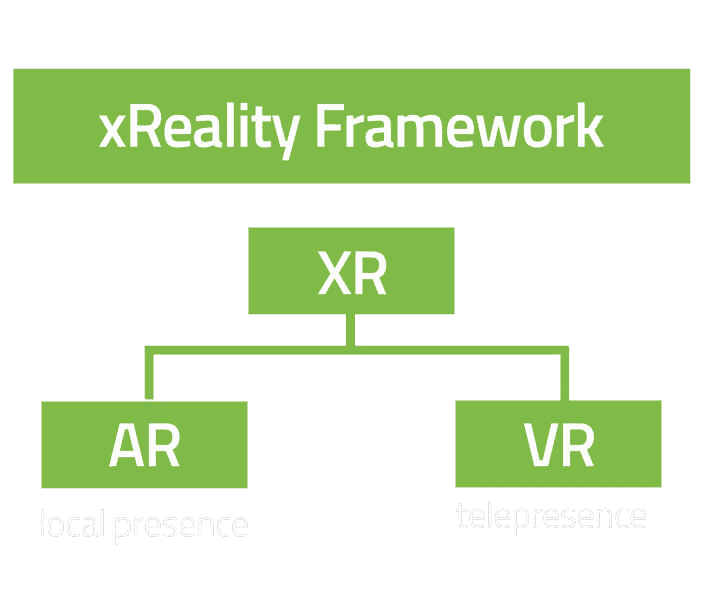
Nowadays the terms AR and VR create clear images in our minds. With virtual reality, we often picture a big clunky headset often used in gaming. With augmented reality, it’s likely a HoloLens from Microsoft or a pair of slim glasses, are barely distinguishable from a standard visual aid. Unfortunately, the distinction is not that simple. Augmented and virtual reality are both on a continuum, which will be briefly explained here. For more details, we recommend our blog post on this topic.
Virtual reality is a simulated experience, tailored specifically to the user, which can be similar to or completely different from the physical world. Virtual reality applications include entertainment, education (e.g., medical or military training), and business (e.g., completely virtual conferences). Widely used VR headsets include HTC-Vive and Oculus Rift.
Augmented reality is an interactive experience created by using the real-world environment and merging it with virtual reality content. AR can, depending on the degree to which both realities are merged, range from Assisted Reality (low) to Mixed Reality (high). An example of assisted reality is a screen placed in a driver’s field of vision, displaying the navigational system. In this use case, virtual and actual reality interact, but they don’t merge on a three dimensional level.
The same example can be turned into mixed reality by moving the navigational directions from an additional screen directly onto the road or other real-life landmarks. The overlaid sensory information can be constructive (i.e., additive to the natural environment) or destructive (i.e., masking the natural environment). This experience is seamlessly interwoven with the physical world so that it is perceived as an immersive aspect of the real environment. Often used hardware here are smartphones or AR glasses such as Microsoft HoloLens.
Mixed Reality is the merging of the real and virtual worlds to create new environments and visualization possibilities where physical and digital objects coexist and interact in real time. Mixed reality does not take place exclusively in either the physical or virtual world, but is a blend of AR and VR. There are many practical uses of mixed reality, such as in design, entertainment, military training, and remote work. There are also various display technologies that facilitate interaction between users and mixed reality applications.
Augmented Reality im Museum revolutioniert das Besuchererlebnis im Meeresmuseum Stralsund, einem Leuchtturm der maritimen Bildung…
Mit einer Augmented Reality Reparatur schnell zurück zur Funktionalität. Dank der Kooperation mit Matrix42 kann…
Mit Gimbel Consulting zusammen entstand ein Projekt zur Standortbegehung und Dokumentation des Zustandes von Mobilfunkstationen….
Die Simon Group hat dank unserer Augmented Reality Software eine Lösung zur Anlagenwartung in Eigenregie…
Thanks to the augmented reality solutions from 3DQR unique customer service can be designed On…
“Highly intelligent, very digital, very modern but also very easy to use” The Association of…











Tell us about your AR ideas now!

Hasselbachplatz 2
39104 Magdeburg | Germany
T: +49 391 556 848 80
M: [email protected]




Hasselbachplatz 2
39104 Magdeburg | Germany
T: +49 391 556 848 80
M: [email protected]
(c) 2024 by 3DQR GmbH